All You Need To Know About Timepieces
The Watch story through out the years
Timekeeping is the measurement and recording of time intervals or durations. It is a fundamental aspect of human civilization, crucial for coordinating activities, scheduling events, and understanding the natural world. The concept of timekeeping has evolved significantly throughout history, with watches being one of the most important inventions in this regard.
Here’s a brief overview of the evolution of watches and timekeeping:
- Sundials: The earliest timekeeping devices were sundials, dating back to ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians and Babylonians. Sundials use the position of the sun’s shadow to estimate the time, and they were widely used in various forms for thousands of years.
- Water Clocks: Water clocks, also known as clepsydrae, were used in ancient civilizations like the Greeks and Chinese. They measured time by the regulated flow of water from one container to another. These devices were relatively accurate but had limitations.
- Mechanical Clocks: The development of mechanical clocks in medieval Europe marked a significant advancement in timekeeping. These clocks used gears, weights, and escapements to regulate the passage of time. The earliest mechanical clocks were large and located in public places like churches and town squares.
- Pocket Watches: During the 16th century, portable timepieces called pocket watches were developed. These watches were often ornate and carried as status symbols by the wealthy. They used mechanical movements and typically had hour and minute hands.
- Wristwatches: Wristwatches emerged in the late 19th century, initially as a practical accessory for military use. Soldiers found them more convenient than pocket watches for checking the time during battle. Wristwatches became popular for civilians during the early 20th century.
- Quartz Watches: The introduction of quartz crystal technology in the 1960s revolutionized timekeeping. Quartz watches use the vibrations of a quartz crystal to maintain highly accurate time. They are more affordable and require less maintenance than traditional mechanical watches.
- Digital Watches: Digital watches, which display the time numerically rather than with analog hands, became popular in the 1970s. They often include additional features like alarms, timers, and electronic displays.
- Smartwatches: In recent years, smartwatches have become increasingly popular. These devices not only tell time but also offer various digital functionalities, such as fitness tracking, notifications, and app integration.
Throughout history, the evolution of timekeeping and watches has been driven by the quest for greater accuracy, portability, and convenience. Today, watches come in a wide range of styles and technologies, catering to both practical timekeeping needs and personal fashion preferences.
Explore different historical periods and their impact on watchmaking, such as ancient civilizations, the Renaissance, the Industrial Revolution, and modern times.
Exploring different historical periods and their impact on watchmaking provides valuable insights into how timekeeping technology has evolved over time. Here’s an overview of how various historical periods have influenced watchmaking:
- Ancient Civilizations (2000 BCE – 500 CE):
- Sundials and Water Clocks: Early timekeeping relied on sundials and water clocks. These inventions helped civilizations like the Egyptians and Babylonians measure time during the day and night.
- Medieval and Renaissance Period (500 – 1600 CE):
- Mechanical Clocks: The Middle Ages saw the development of mechanical clocks in European monasteries and cathedrals. These large clocks marked the hours and played a crucial role in organizing daily life.
- Miniaturization: As the Renaissance period unfolded, watchmakers began to miniaturize clocks, leading to the development of the first pocket watches in the 16th century.
- 17th to 18th Centuries:
- Precision and Accuracy: Advances in metallurgy and precision engineering improved the accuracy of mechanical watches. Watchmakers like John Harrison worked on solving the problem of determining longitude at sea, leading to the creation of marine chronometers.
- 19th Century – Industrial Revolution:
- Mass Production: The Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in watchmaking. Innovations like interchangeable parts and the assembly line made watches more affordable and accessible to the middle class.
- Railroad Watches: During this period, accurate timekeeping became crucial for the growing railway networks. “Railroad watches” were designed to meet stringent accuracy standards for train schedules.
- 20th Century – Modern Times:
- Wristwatches: The early 20th century witnessed the widespread adoption of wristwatches, largely driven by their use in military contexts during World War I. They gradually became a fashion statement and a symbol of personal style.
- Quartz Revolution: In the 1960s and 1970s, quartz technology revolutionized watchmaking. Quartz watches, powered by batteries and utilizing quartz crystal oscillations, offered superior accuracy and durability.
- Digital and Smartwatches: The late 20th century and beyond saw the emergence of digital watches, which displayed time electronically. In recent years, smartwatches have combined timekeeping with a range of digital features and connectivity.
- Contemporary Watchmaking (21st Century):
- High-End Mechanical Watches: Despite the rise of digital and smartwatches, traditional mechanical watchmaking remains highly regarded among collectors and connoisseurs. Luxury watchmakers continue to craft intricate timepieces by hand.
- Innovations in Materials and Design: Advancements in materials like ceramics, carbon composites, and exotic metals have expanded the design possibilities for modern watches.
- Sustainability: There’s a growing emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendliness in watchmaking, with some brands focusing on recycled materials and responsible manufacturing.
Each historical period has contributed to the evolution of watchmaking, shaping the industry’s technology, design, and cultural significance. Today, watches are not just timekeeping devices but also expressions of art, craftsmanship, and technological prowess.
Notable watchmakers and brands that have made significant contributions to the industry. Discuss their history, innovations, and iconic timepieces
Numerous watchmakers and brands have made significant contributions to the watchmaking industry throughout history. Here are some notable ones, along with their history, innovations, and iconic timepieces:
- Patek Philippe:
- History: Founded in 1839 in Geneva, Switzerland, Patek Philippe is one of the world’s most prestigious watchmakers. It has a rich history of crafting exquisite timepieces for royalty, celebrities, and watch aficionados.
- Innovations: Patek Philippe is known for its innovations in watchmaking, including the first wristwatch with a perpetual calendar in 1925 and the first wristwatch with a minute repeater in 1989.
- Iconic Timepiece: The Patek Philippe Calatrava, first introduced in 1932, is a classic dress watch known for its timeless elegance and simplicity. The Patek Philippe Nautilus, introduced in 1976, is another iconic model, renowned for its sporty design.
- Rolex:
- History: Founded in London in 1905, Rolex is one of the most recognized and influential watch brands in the world. It relocated to Geneva, Switzerland, shortly after its inception.
- Innovations: Rolex has been at the forefront of several key innovations, including the first waterproof wristwatch, the Oyster, in 1926, and the development of the self-winding automatic movement.
- Iconic Timepiece: The Rolex Submariner, introduced in 1953, is an iconic dive watch recognized for its durability and classic design. The Rolex Daytona, famous for its association with motorsports, is another highly sought-after model.
- Audemars Piguet:
- History: Founded in 1875 by Jules-Louis Audemars and Edward-Auguste Piguet, Audemars Piguet is renowned for its luxury watchmaking. The company remains family-owned to this day.
- Innovations: Audemars Piguet is known for its pioneering spirit and innovations in watch complications. They introduced the world’s first minute-repeating wristwatch in 1892 and developed the Royal Oak, a stainless steel luxury sports watch, in 1972.
- Iconic Timepiece: The Audemars Piguet Royal Oak is an iconic model known for its distinctive octagonal bezel and integrated bracelet. It helped redefine the luxury sports watch category.
- Omega:
- History: Founded in 1848 in Switzerland, Omega has a long history of precision and innovation. It has been the official timekeeper for the Olympics and has supplied watches to NASA.
- Innovations: Omega is known for its role in space exploration, with the Omega Speedmaster becoming the first watch on the moon during the Apollo 11 mission in 1969. They are also renowned for their Co-Axial escapement technology, which reduces friction in the movement.
- Iconic Timepiece: The Omega Speedmaster Professional, often referred to as the “Moonwatch,” is one of the most iconic watches in history due to its lunar landing association.
- Swatch:
- History: Founded in 1983 as a response to the “quartz crisis,” Swatch aimed to revitalize the Swiss watch industry with affordable and colorful quartz watches.
- Innovations: Swatch brought innovation through its vibrant designs, use of plastic materials, and assembly line production, making Swiss watches more accessible to a wider audience.
- Iconic Timepiece: The original Swatch Watch, characterized by its colorful and playful design, became an icon of 1980s fashion and pop culture.
These watchmakers and brands have left indelible marks on the watchmaking industry, pushing the boundaries of craftsmanship, technology, and design, and creating timepieces that are celebrated for their artistry and innovation.
The key technological advancements that have shaped the development of watches, such as the invention of the mechanical movement, the introduction of quartz watches, and the rise of smartwatches.
Key technological advancements have played a pivotal role in shaping the development of watches over the years. Here are three significant milestones in watch technology:
- Invention of the Mechanical Movement:
- Overview: The invention of the mechanical movement marked a fundamental shift in timekeeping technology. Mechanical watches rely on intricate systems of gears, springs, and escapements to measure time.
- Impact: Mechanical watches allowed for more accurate and reliable timekeeping compared to earlier methods like sundials and water clocks. They also enabled the miniaturization of timekeeping devices, leading to the development of pocket watches and wristwatches.
- Innovation: Over centuries, watchmakers improved mechanical movements, introducing features like the balance wheel and hairspring for greater precision. The development of the mainspring and the escapement mechanism contributed to consistent power delivery, further enhancing accuracy.
- Introduction of Quartz Watches:
- Overview: The introduction of quartz technology in watchmaking revolutionized timekeeping. Quartz watches use the vibrations of a quartz crystal to regulate the movement of a timekeeping mechanism.
- Impact: Quartz watches brought unprecedented accuracy and affordability to the market. They were far more precise than mechanical watches, with an accuracy of a few seconds per month, and they required minimal maintenance.
- Innovation: The first commercially available quartz watch, the Seiko Astron, was introduced in 1969. This development was a result of miniaturizing quartz crystal oscillators and using electronic circuits to divide time accurately. The quartz revolution led to a global industry shift, with many traditional mechanical watchmakers incorporating quartz technology into their product lines.
- Rise of Smartwatches:
- Overview: Smartwatches represent the latest phase of watch technology, combining timekeeping with digital functionalities and connectivity to other devices.
- Impact: Smartwatches have expanded the role of timepieces from simple timekeeping to serving as personal digital assistants. They can track fitness, provide notifications, offer GPS navigation, and more.
- Innovation: Companies like Apple, Samsung, and Garmin have been at the forefront of the smartwatch revolution. Key innovations include touchscreens, app ecosystems, heart rate monitors, built-in GPS, and integration with smartphones. The development of more efficient processors and longer-lasting batteries has also been crucial to the success of smartwatches.
These technological advancements have not only enhanced the accuracy and functionality of watches but have also transformed the way we interact with timekeeping devices. From the precision of mechanical movements to the accessibility of quartz watches and the multifunctionality of smartwatches, each era of innovation has left an indelible mark on the watch industry, catering to a wide range of preferences and needs.
The famous and influential watches throughout history. Discuss their design, features, and the impact they had on watchmaking and popular culture.
Here are some famous and influential watches throughout history, along with their design, features, and their impact on watchmaking and popular culture:
- Rolex Submariner:
- Design: The Rolex Submariner, introduced in 1953, is an iconic dive watch known for its timeless design. It features a robust stainless steel case, a unidirectional rotating bezel, and luminous markers and hands for excellent legibility underwater.
- Features: The Submariner was one of the first watches to offer water resistance up to 100 meters. It also included a self-winding movement, allowing it to run without a battery or manual winding.
- Impact: The Rolex Submariner played a significant role in popularizing dive watches and is often considered the archetype of this watch category. It has been worn by numerous celebrities, further enhancing its status as a symbol of luxury and adventure.
- Omega Speedmaster Professional (“Moonwatch”):
- Design: The Omega Speedmaster, introduced in 1957, has a distinctive chronograph design with its three sub-dials and tachymeter scale on the bezel. Its black dial and white hands and indices are instantly recognizable.
- Features: The Speedmaster became famous for being the first watch on the moon during NASA’s Apollo 11 mission in 1969. It has a manual-winding chronograph movement and is known for its durability in extreme conditions.
- Impact: The “Moonwatch” is a legendary timepiece, celebrated for its association with space exploration. It has a dedicated following among space enthusiasts and collectors and remains one of Omega’s most iconic models.
- Patek Philippe Calatrava:
- Design: The Patek Philippe Calatrava, first introduced in 1932, is known for its elegant and minimalist design. It typically features a round case, simple dial, and slim hands and markers.
- Features: The Calatrava embodies the essence of a classic dress watch, offering a manual-winding or automatic movement with precision and reliability.
- Impact: The Calatrava exemplifies timeless sophistication and has become a symbol of luxury and refinement. It has influenced the design of countless dress watches and remains a coveted piece in high-end watch collections.
- Audemars Piguet Royal Oak:
- Design: The Audemars Piguet Royal Oak, introduced in 1972, is known for its bold and distinctive design. It features an octagonal bezel with exposed screws, an integrated bracelet, and a “tapisserie” dial pattern.
- Features: The Royal Oak was one of the first luxury sports watches made of stainless steel. It houses an automatic movement and offers a blend of sportiness and elegance.
- Impact: The Royal Oak is credited with pioneering the luxury sports watch category. Its audacious design challenged traditional notions of high-end watch materials, making stainless steel a prestigious choice in watchmaking.
- Apple Watch:
- Design: The Apple Watch, first released in 2015, features a sleek, rectangular design with a customizable digital display. It comes in various materials and bands to suit individual preferences.
- Features: The Apple Watch combines timekeeping with a wide range of digital functionalities, including fitness tracking, notifications, GPS navigation, and integration with Apple’s ecosystem.
- Impact: The Apple Watch has had a profound impact on the watch industry and popular culture by redefining what a watch can do. It has spurred the growth of the smartwatch market and encouraged traditional watchmakers to explore smartwatch offerings.
These watches have left an indelible mark on the world of horology, not only for their design and features but also for the cultural and historical significance they carry. They continue to inspire watch enthusiasts and collectors, shaping the future of watchmaking.
The different watch styles and trends that emerged over time, such as pocket watches, wristwatches, dress watches, sports watches, and luxury timepieces.
Watches come in various styles and have evolved over time to cater to different needs and preferences. Here are some of the key watch styles and trends that have emerged over time:
- Pocket Watches:
- Era: 16th century onwards, with peak popularity in the 19th and early 20th centuries.
- Design: Pocket watches were originally designed as portable timepieces, often enclosed in protective cases. They featured intricate engravings and were often worn with a chain attached to a vest or belt loop.
- Usage: Pocket watches were the standard timekeeping devices for centuries, used by both men and women. They were particularly popular among the upper class and were often considered a symbol of refinement and sophistication.
- Wristwatches:
- Era: Late 19th century, gained popularity in the early 20th century.
- Design: Wristwatches were initially designed as practical tools for military use, so they were typically rugged and utilitarian. Over time, they evolved into various styles, including dress watches and sports watches.
- Usage: Wristwatches became popular during World War I when soldiers found them more convenient than pocket watches on the battlefield. They eventually transitioned from military gear to everyday fashion accessories for both men and women.
- Dress Watches:
- Design: Dress watches are characterized by their elegant and minimalist designs. They typically feature thin cases, simple dials, and slim hands and markers. Precious metals like gold and platinum are often used in their construction.
- Usage: Dress watches are designed to complement formal attire and are suitable for special occasions and business settings. They are prized for their understated sophistication and are often handed down as heirlooms.
- Sports Watches:
- Design: Sports watches are designed for durability and functionality. They often have features like water resistance, shock resistance, and additional complications such as chronographs (stopwatches) and tachymeters (speed measurements).
- Usage: Sports watches cater to various outdoor and athletic activities, including diving, aviation, racing, and more. Iconic examples include the Rolex Submariner for diving and the Omega Speedmaster for space exploration.
- Luxury Timepieces:
- Design: Luxury timepieces are characterized by their high-quality materials, craftsmanship, and attention to detail. They often incorporate precious metals, gemstones, and intricate complications.
- Usage: Luxury watches are status symbols and collectible items. They are often worn by celebrities and high-net-worth individuals. Brands like Patek Philippe, Audemars Piguet, and Rolex are known for their luxury timepieces.
- Smartwatches:
- Design: Smartwatches combine traditional watch elements with digital technology. They have touchscreen displays and offer various digital features, such as fitness tracking, app integration, and notifications.
- Usage: Smartwatches have gained popularity as versatile wearable devices that cater to a wide range of lifestyles. They are popular among tech enthusiasts, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone seeking seamless connectivity.
- Vintage and Retro Watches:
- Design: Vintage and retro watches refer to timepieces from previous eras, often featuring design elements that evoke nostalgia. These watches can range from mid-20th-century classics to 1980s and 1990s retro styles.
- Usage: Vintage and retro watches are collected by enthusiasts who appreciate the history and aesthetics of older timepieces. They often carry unique charm and character.
Watch styles and trends continue to evolve with changing fashion preferences, technological advancements, and cultural influences. Today, there is a vast array of watches to suit different tastes, occasions, and lifestyles, reflecting the rich diversity within the world of horology.
The materials used in watchmaking, including precious metals, gemstones, and innovative materials. Highlight the craftsmanship involved in creating intricate watch movements and intricate designs.
Materials used in watchmaking play a critical role in both the aesthetics and functionality of timepieces. Watchmakers often use a combination of traditional and innovative materials to craft their creations. Here’s an overview of some of the materials used in watchmaking and the craftsmanship involved in creating intricate watch movements and designs:
1. Precious Metals:
- Materials: High-end watches frequently use precious metals such as gold (yellow, white, or rose), platinum, and occasionally, silver. These materials lend a luxurious and elegant appearance to watch cases and bracelets.
- Craftsmanship: Craftsmen skillfully work with these metals to create cases, dials, and hands. Intricate techniques like guilloché engraving and gemstone setting are often employed to enhance the aesthetic appeal of these components.
2. Stainless Steel:
- Materials: Stainless steel is a common material for watch cases and bracelets, known for its durability, resistance to corrosion, and affordability.
- Craftsmanship: Craftsmen employ precision machining and finishing techniques to create stainless steel cases with polished, brushed, or satin finishes, depending on the desired look.
3. Titanium:
- Materials: Titanium is valued for its strength, lightweight properties, and hypoallergenic qualities. It is often used in sports and adventure watches.
- Craftsmanship: Craftsmen use specialized machining techniques to work with titanium, ensuring its strength while maintaining a lightweight profile. Titanium watches may feature coatings for added scratch resistance.
4. Ceramic:
- Materials: Ceramic, particularly high-tech ceramic, is used for watch cases and sometimes bracelets. It is prized for its scratch resistance, durability, and deep color options.
- Craftsmanship: Creating ceramic watch components involves precision molding and high-temperature firing processes. The material is then polished to achieve a glossy finish.
5. Sapphire Crystal:
- Materials: Sapphire crystal is commonly used for watch crystals due to its exceptional hardness and scratch resistance.
- Craftsmanship: Craftsmen cut and shape sapphire crystals to precise dimensions. These crystals may be treated with anti-reflective coatings to improve readability.
6. Gemstones:
- Materials: Gemstones like diamonds, sapphires, emeralds, and rubies are often used as hour markers, bezel accents, or even as entire watch dials.
- Craftsmanship: Gemstone setting is a highly specialized skill involving precise cutting and placement of stones. Setting techniques include pave, channel, and bezel settings, depending on the design.
7. Innovative Materials:
- Materials: Watchmakers also experiment with innovative materials such as carbon fiber, ceramic composites, and high-performance polymers to create lightweight, durable, and technologically advanced components.
- Craftsmanship: Working with innovative materials often requires specialized knowledge and machinery. Craftsmen employ cutting-edge techniques to shape, mold, and assemble these materials into watch components.
8. Watch Movements:
- Materials: Inside the watch case, the movement is the heart of the timepiece. It consists of various materials, including metal alloys for gears, springs (usually made of steel), and synthetic rubies as bearing jewels.
- Craftsmanship: Creating a watch movement involves intricate craftsmanship. Watchmakers meticulously assemble and adjust hundreds of tiny components, ensuring precision and reliability. Fine-tuning and testing are critical to achieving accurate timekeeping.
In watchmaking, the choice of materials and the craftsmanship involved in working with them are essential factors in creating both the functional and aesthetic aspects of timepieces. These materials, whether traditional or innovative, contribute to the artistry and durability of watches while reflecting the brand’s design philosophy and values.
How watches have played a role in historical events, such as aviation, exploration, military operations, and sports.
Watches have played pivotal roles in historical events across various domains, contributing to aviation, exploration, military operations, and sports. Here’s how they have made a significant impact in these contexts:
1. Aviation:
- Role: Watches were critical tools for early aviators who needed precise timekeeping for navigation and flight planning. Accurate time measurements were essential for calculating speed, distance, and fuel consumption.
- Famous Example: The Longines Lindbergh Hour Angle Watch was created in collaboration with Charles Lindbergh, the first person to complete a solo nonstop transatlantic flight in 1927. This watch allowed Lindbergh to calculate his longitude accurately during his historic flight.
2. Exploration:
- Role: Watches were indispensable for explorers embarking on treacherous journeys to uncharted territories. They helped explorers keep track of time and coordinate their expeditions.
- Famous Example: In 1769, Captain James Cook embarked on his first voyage to the South Pacific, equipped with a marine chronometer created by John Harrison. This chronometer allowed Cook to accurately determine his ship’s longitude, greatly enhancing navigation during exploration.
3. Military Operations:
- Role: Watches have been vital tools for military personnel in coordinating operations, synchronizing attacks, and timing maneuvers. They were especially crucial during wartime.
- Famous Example: During World War I, wristwatches gained popularity among soldiers because they were more practical than pocket watches on the battlefield. The “trench watch” was born, with luminous dials for nighttime visibility.
4. Sports:
- Role: Timing accuracy is crucial in various sports, from racing to diving. Watches designed for specific sports often feature features such as chronographs and tachymeters to help athletes measure performance.
- Famous Example: Omega’s involvement as the official timekeeper for the Olympic Games dates back to 1932. Their timing technology has been crucial in determining world records and achieving fair competition in various sports.
5. Space Exploration:
- Role: Watches were instrumental in space missions, as astronauts needed reliable timekeeping devices for mission coordination and for performing precise calculations.
- Famous Example: The Omega Speedmaster Professional, often referred to as the “Moonwatch,” was worn by astronauts during NASA’s Apollo missions, including the historic Apollo 11 mission that landed the first humans on the moon in 1969.
6. Underwater Exploration:
- Role: Divers rely on watches with water-resistant features and precise timekeeping to monitor dive durations and decompression stops.
- Famous Example: The Rolex Submariner, introduced in 1953, quickly became a favorite among professional divers for its water resistance and durability.
In each of these historical contexts, watches served as essential tools, contributing to the success and safety of various endeavors. Their accuracy, durability, and functionality made them indispensable for those who ventured into the unknown, engaged in military operations, explored the depths of the sea, or aimed to break records in sports and aviation. As a result, watches continue to be regarded not only as timekeeping instruments but also as symbols of human achievement and exploration.
Watch collecting,
including tips for beginners, notable collectors, and the value of vintage and rare watches.
Watch collecting is a passionate and rewarding hobby for enthusiasts who appreciate the craftsmanship, history, and artistry of timepieces. Here’s some information on watch collecting, including tips for beginners, notable collectors, and the value of vintage and rare watches:
Tips for Beginners in Watch Collecting:
- Educate Yourself: Start by learning about the different types of watches, brands, and their histories. Familiarize yourself with key terminology and understand what makes a watch valuable.
- Set a Budget: Determine how much you’re willing to invest in watch collecting. Watches can vary widely in price, so it’s essential to establish a budget that suits your financial situation.
- Research Brands and Models: Explore various watch brands and models to find ones that resonate with your style and interests. Research the reputation and reliability of brands and their resale value.
- Condition Matters: Pay close attention to the condition of a watch. Vintage and pre-owned watches may have wear and tear, so assess their maintenance history and any necessary repairs.
- Seek Authenticity: Ensure that the watch is authentic and comes with proper documentation and provenance. Beware of counterfeit or replica watches.
- Join Watch Communities: Engage with other watch collectors through forums, social media groups, and local watch clubs. You can learn from experienced collectors and gain insights into the market.
- Patience is Key: Be patient in building your collection. Rushing into purchases may lead to regrets. Take your time to find the right pieces for your collection.
- Buy What You Love: Collect watches that genuinely appeal to you, whether for their design, historical significance, or technical prowess. Your passion will make your collection more enjoyable.
Notable Watch Collectors:
- Eric Clapton: The famous musician and guitarist has one of the most extensive and valuable watch collections globally, featuring rare vintage and modern timepieces.
- Paul Newman: The iconic actor and racecar driver was known for his love of Rolex watches, and the Rolex Daytona with his name on it (the “Paul Newman Daytona”) has become legendary in the world of horology.
- James Ward Packard: The American automobile manufacturer was an avid watch collector during the early 20th century. He commissioned Patek Philippe and Vacheron Constantin to create custom watches, and many of his pieces are now highly sought after.
- Phillip Schaffhausen: The founder of IWC Schaffhausen, a prominent Swiss watchmaker, was known for his extensive collection of vintage and historical timepieces.
The Value of Vintage and Rare Watches:
- Rarity: Vintage and rare watches often have limited production numbers, making them highly sought after by collectors. Limited editions, discontinued models, and unique features can drive up their value.
- Historical Significance: Watches with historical connections, such as those worn by famous individuals or used in significant events, can fetch high prices due to their historical relevance.
- Condition: The condition of a vintage watch significantly impacts its value. Well-preserved watches with original parts and minimal wear tend to command higher prices.
- Brand Reputation: Watches from prestigious brands like Rolex, Patek Philippe, and Audemars Piguet tend to hold their value and appreciate over time due to their craftsmanship and brand heritage.
- Collector Demand: The watch collecting community’s demand for specific models or brands can drive up prices at auctions and in the secondary market.
- Provenance: Watches with documented provenance, such as original purchase receipts, service records, and ownership history, often command higher prices due to their authenticity and traceable history.
In conclusion, watch collecting is a fascinating hobby that combines history, art, and craftsmanship. Beginners should start by educating themselves, setting a budget, and researching watches that align with their preferences. Notable collectors and the value of vintage and rare watches illustrate the allure and investment potential of this hobby. Whether you’re drawn to vintage classics or contemporary masterpieces, watch collecting offers a world of discovery and appreciation for horological artistry.
Current trends and future possibilities in watchmaking, such as advancements in smartwatches, sustainability in the industry, and the fusion of traditional craftsmanship with modern technology.
The future of watchmaking is shaped by a combination of technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and sustainability considerations. Here are some key trends and possibilities for the future of watches:
1. Advancements in Smartwatches:
- Continued Integration: Smartwatches are likely to become more integrated into our daily lives, with increased connectivity to smartphones, smart homes, and other devices. They will offer a wide range of functionalities beyond basic notifications and fitness tracking.
- Health and Wellness: Smartwatches will increasingly focus on health monitoring, offering features like continuous glucose monitoring, blood pressure measurement, and improved sleep tracking.
- Customization: Manufacturers may emphasize personalization, allowing users to customize not only watch faces but also watch bands, materials, and other aspects of their smartwatches.
- Battery Life: Enhancements in battery technology will be crucial to extending the battery life of smartwatches, reducing the need for frequent recharging.
2. Sustainability in the Industry:
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Watchmakers are likely to explore more sustainable materials for watch components, including recycled metals, eco-friendly plastics, and biodegradable materials.
- Ethical Sourcing: Ethical and responsible sourcing of materials, such as gemstones and precious metals, will be a focus to reduce the environmental and social impact of the industry.
- Energy Efficiency: Efforts to improve the energy efficiency of watches, especially in smartwatches, will continue to reduce the environmental footprint of these devices.
- Repairability: Manufacturers may prioritize designs that make watches easier to repair and maintain, reducing the need for disposal and encouraging longevity.
3. Fusion of Traditional Craftsmanship with Modern Technology:
- Hybrid Watches: The fusion of traditional watchmaking with modern technology is likely to result in hybrid watches that combine mechanical movements with smart features. These watches offer the elegance of traditional craftsmanship with digital functionalities.
- Innovative Materials: Watchmakers will continue to experiment with innovative materials, combining traditional watchmaking expertise with advanced composites, ceramics, and high-tech alloys.
- Craftsmanship and Design: High-end watchmakers will maintain a strong focus on craftsmanship, creating intricate and artistic timepieces. These will appeal to collectors who appreciate both tradition and innovation.
- Mechanical Excellence: The art of traditional watchmaking, including the creation of complex complications and hand-finished movements, will remain a hallmark of luxury watches.
4. Sustainable Practices:
- Recycling and Reuse: Watch brands may increasingly adopt recycling and refurbishment programs to extend the lifespan of their products and reduce waste.
- Reduced Packaging: There will be a push toward eco-friendly packaging, with brands using sustainable materials and minimizing excess packaging.
- Carbon Neutrality: Some watchmakers may aim for carbon neutrality in their production processes, supply chains, and operations.
5. Integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
- Virtual Try-On: AR and VR technologies may be used to create virtual showrooms and allow customers to “try on” watches online before making a purchase.
- Training and Maintenance: Watchmakers and technicians may use AR and VR for training purposes and remote maintenance and repair assistance.
The future of watches is a dynamic blend of tradition and innovation, with smartwatches continually evolving, sustainable practices becoming more prevalent, and traditional craftsmanship embracing modern technologies. As consumers demand more functionality, sustainability, and personalization from their timepieces, watchmakers will continue to adapt to meet these expectations while preserving the artistry and heritage of watchmaking.
Watches have been around for centuries and have gone through many changes over time. Here’s a brief overview of the history of watches:
- Early Timepieces: The earliest timepieces were sundials, which used the sun’s position in the sky to tell time. Later, water clocks were developed, which used the flow of water to measure time.
- Pocket Watches: The first portable timepieces were pocket watches, which were invented in the 16th century. They were small and could be carried in a pocket, but they were expensive and only affordable for the wealthy.
- Wristwatches: Wristwatches were first developed in the late 19th century as a more convenient way to tell time. They became popular during World War I when soldiers found them more practical than pocket watches.
- Quartz Watches: In the 1960s, quartz watches were introduced, which used electronic oscillators to keep time. They were more accurate than mechanical watches and became popular in the 1970s.
- Smartwatches: In recent years, smartwatches have become popular. They connect to a smartphone and can display notifications, track fitness, and perform other functions.
The ancient civilizations used the sun and moon to determine the time and date. Then the sundial (the shadow clock) was the first device used to measure the time. More than 5000 years ago the ancient Egyptian created the oldest known shadow clock (obelisks).
The Egyptian shadow clock divided the day time into 10 parts. The obelisks were the first device to use the AM and PM system. Also the Egyptian developed different timekeeping instruments which included water clock (Clepsydrae) (see the details in the ancient Egyptian page).
Andronicus of Cyrrhus, supervised the Tower of the Winds in Athens more than 2000 ago and the Roman adopted the same way later on.
In the 16the century pocket watches were invented in Tudor, England, in the beginning, it was large and were generally worn around the neck. Not until the 19th Century when the rest watches invented by Patek Philippe and start to show on the women rest as the men still using the pocket watches.
Clocks and Watches are devices used for thousands of years to measure or indicate the passage of time.
A clock, which is larger than a watch, is usually intended to be kept in one place. The watch is designed to be carried or worn. Both types of timepieces require a source of power and a means of transmitting and controlling it, as well as indicators to register the lapse of time units.
The current system we use to measure the time go back to approximately 2000 BC (dated to the Ancient Egyptians), who divided the day into two 12-hour periods.
During the nineteenth century when the pocket watches were the standard, in the twentieth century the watch maker start introduce smaller models designed to be worn by ladies on a neck chain or as a pendant
Today’s watches are usually small and delicate in nature, yet durable enough to withstand the normal abuse of daily use.
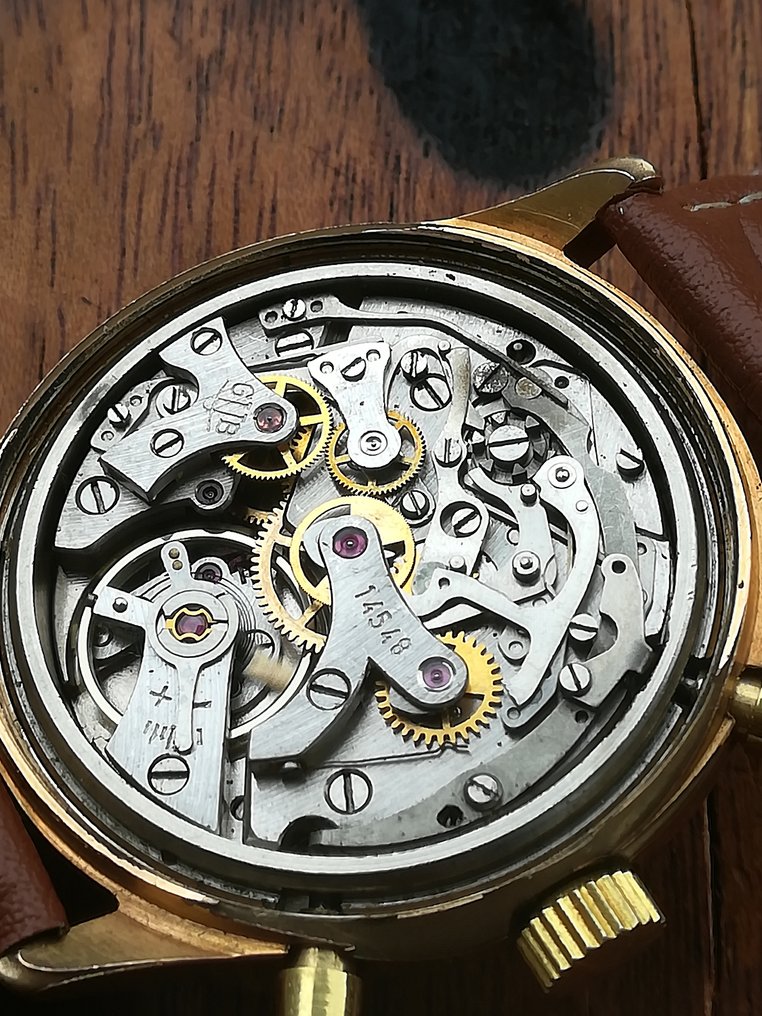
Watch movement is powered by springs and regulated by an escapement that must be of the balance-wheel style, rather than the pendulum, so that the watch will continue to run when moved or turned in various positions
Here is more information about this devices and the history behind it, if you like to know more details. So many watches out there can make you confused as to which kind of watch to go for!
There are two main types of watches- the mechanical watch and the quartz watch. Let’s look at them in detail. For thousands of years, devices have been used to measure and keep track of time
Please remember that this is an unofficial account of the history of this company, Should you happen to find any mistakes with our information then please let us know at
watchcue.com
Seiko is a Japanese watch company that was founded in Tokyo in 1881 when Kintaro Hattori opened a watch and jewelry shop in the Ginza area of Tokyo, Japam. Eleven years later hebegan to produce clocks under the name Seikosha. According to Seiko’s official company history, titled “A Journey In Time: The Remarkable Story of […]
TAG Heuer is a luxury watch brand that has been around for over 150 years. The brand has established itself as a leader in the watch industry by producing high-quality timepieces that are both stylish and functional. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at TAG Heuer watches and why they are […]
Timex is an American watch brand that was founded in 1854. The brand is known for producing high-quality, reliable watches that are affordable and accessible to a wide range of consumers. Timex has a wide range of watches, including dress watches, sports watches, and digital watches. The brand’s watches are known for their durability and […]
Victorinox Swiss Army is a Swiss brand that is known for producing high-quality knives, watches, and other products. The company was founded in 1884 in Switzerland, and it has since become famous for its durable and reliable Swiss Army knives. In addition to its knives, Victorinox Swiss Army also produces a range of high-quality watches. […]
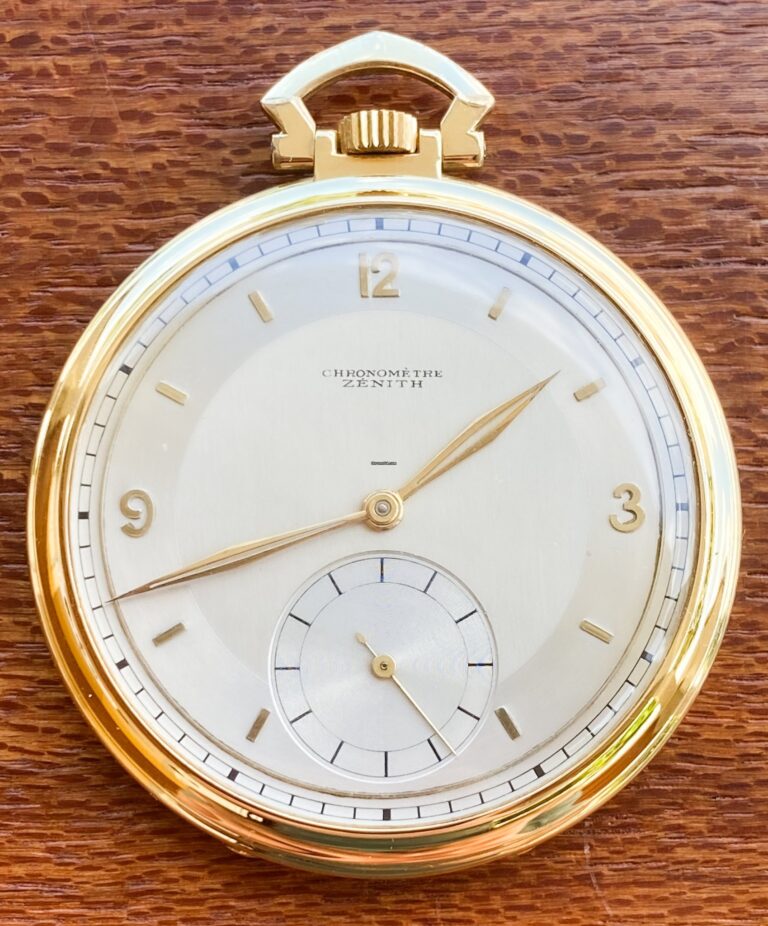
Zenith is a Swiss luxury watch brand that was founded in 1865 in Le Locle, Switzerland. The company is known for producing high-quality watches with precision engineering and elegant designs. Zenith has a long history of innovation in the watch industry, and it has won numerous awards for its timepieces. One of Zenith’s most famous […]
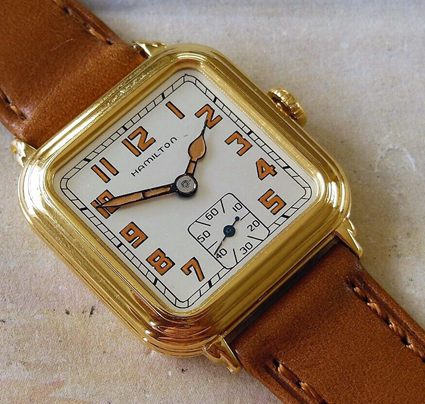
Hamilton Watch Company is an American brand of wristwatches founded in 1892 in Lancaster, Pennsylvania. The company has a rich history and has played a significant role in the development of the American watchmaking industry. Here are some key moments in the history of Hamilton watches: The company produced its first series of pocket watches, […]
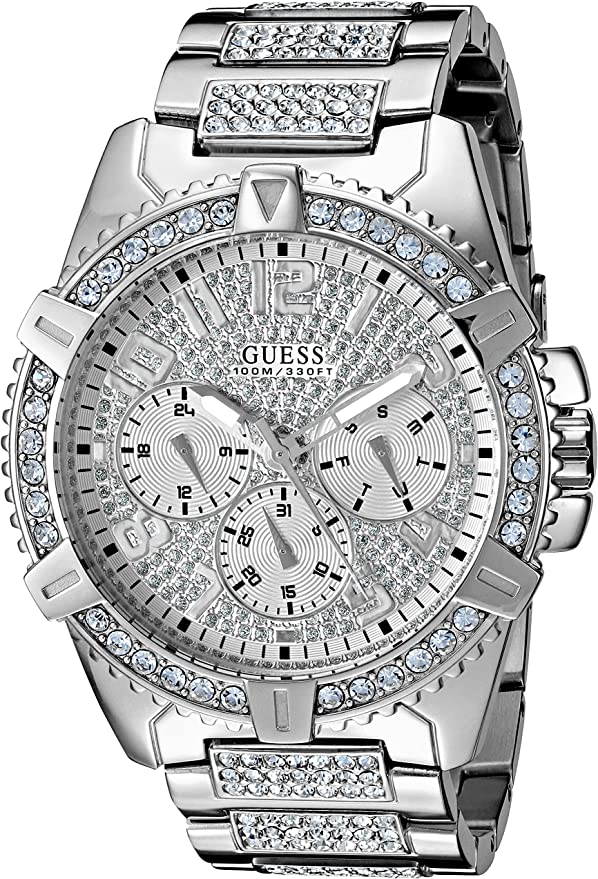
Guess is a fashion brand that was founded in 1981 by the Marciano brothers, Maurice and Paul, in Los Angeles, California. The brand started as a denim company, but quickly expanded to include other fashion products such as watches. The first Guess watches were introduced in 1984, featuring a bold and trendy style that appealed […]
Glashütte Original’s roots stretch all the way back to 1845. More than 175 years ago, the first watchmakers came to Glashütte in Saxony to manufacture watch parts and watches in the small town. The Glashütte watch soon became a byword for high quality worldwide. Glashütte Original is descended from this tradition of precise, elegant craftsmanship, […]
In 1894 It was founded in by German-born watchmaker Dietrich Grün. Gruen Watch Company was formerly one of the largest watch manufacturers in the United States and was in business from about 1894 to 1958 and was in Cincinnati, Ohio. Gruen was one of the first US watch companies to offer basic movements produced in […]
Founded by a master watchmaker name Georges Graham in 1695in London, United Kingdom . he invent the pendulum system made from mercury forenabling a clock to keep accurate time despite temperature increases ordecreases. He also created the first stopwatch. Today Graham watches located at the company’s La Choux deFonds manufacturing facilities in Switzerland. In 1715 […]
Glycine used extensively in commercial and military aviation. Glycine used during World War II by the German army for its land forces and United States Air Force pilots during the Vietnam War and astronaut Pete Conrad during the Gemini 5 and Gemini 11 spaceflights. The design allowed servicemen to simultaneously know the time at home […]
Glashütte Original watches are one of the most highly respected luxury watch brands within the watchmaking community. Each Glashütte Original timepiece offers a unique balance of premiere elegance and innovative functionality. For nearly two centuries, the German luxury watch manufacturer Glashütte Original has stood for exceptional quality and an expert eye for detail. Although it’s […]
In 1791 Jean-François Butte began crafting high-end timepieces. In 1852 when Constant Girard founded the company Girard & Campagnie. In 1856 He marry Marie Perregaux, a member of an established family of watchmakers from Le Locle. The respective surnames of the couple were combined to form Manufacture Girard-Perregaux, This name lives on to this day. […]
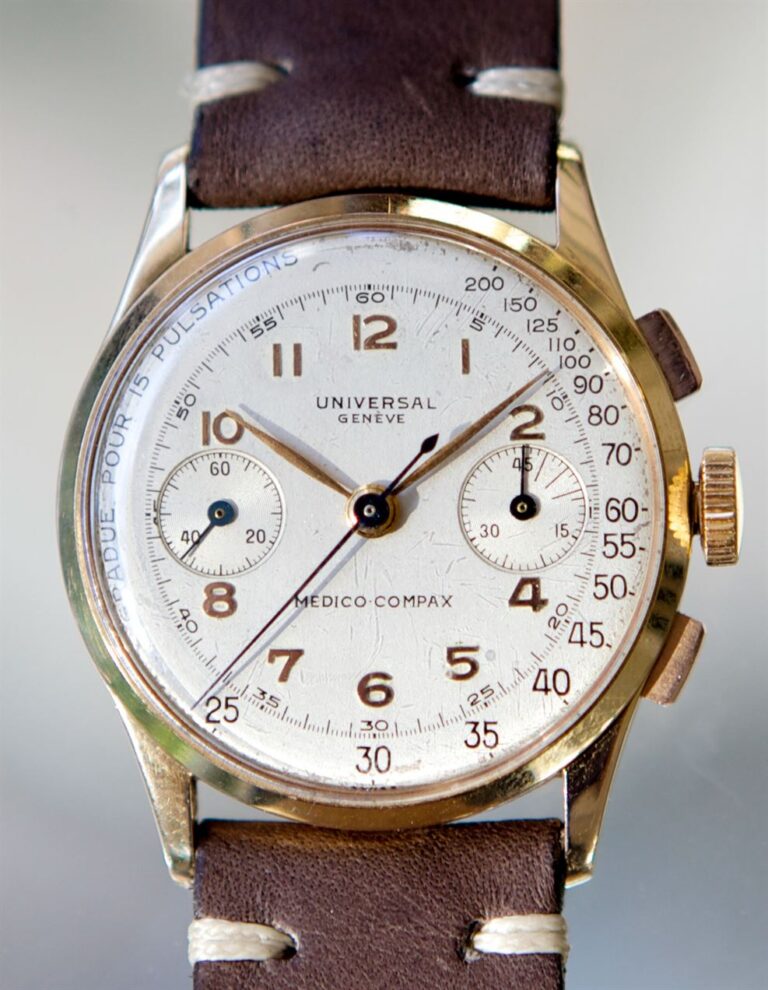
Genève watches Swiss luxury watch company founded in 1894 based in Le Locle by co-founder Ulysse Perret as Universal Watch. From beginnings, the company has produced complete watches with in-house movements’. Throughout the 20th century, distributed many notable and important timepieces. Along with neighboring Geneva great timepieces watch companies, Universal is internationally regarded for its […]
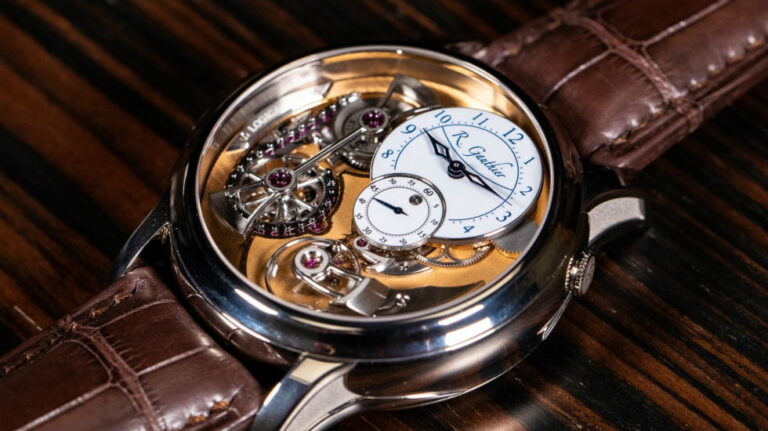
Romain Gauthier was born in 1975 in the Vallée de Joux, Switzerland, the cradle of fine Swiss watchmaking. It was here that Romain developed his passion for traditional Haute Horlogerie, his grasp of mechanics and engineering, and his eye for design. Having specialised in precision mechanics at technical college, Romain qualified as a constructor of […]
Gallet History Time Line 1466 Humbertus Gallet, living and working in Geneva, becomes acitizen of the republic on the 18th of April. Historical references point tohis profession as a horloger or clock maker. 1685 Due to the abolishment by French King Louis XIV of thetolerance agreement of Nantes, additional members of […]
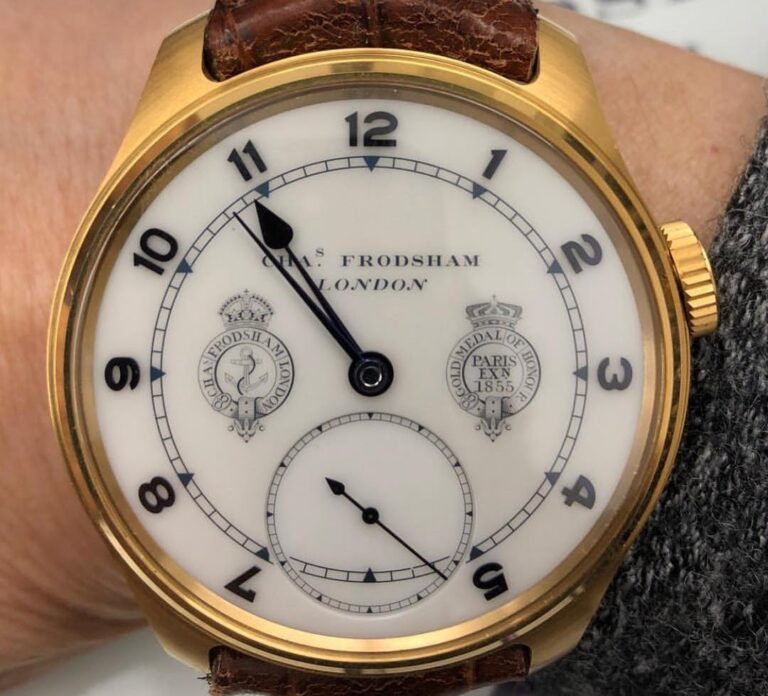
Charles Frodsham & Co is the oldest chronometer manufacturers in the world – 1834 Charles Frodsham 1810 – 1871) was a distinguished English horologist, establishing the firm of Charles Frodsham & Co, which remains in existence as the longest continuously trading firm of chronometer manufacturers in the world. In 2018, the firm launched a new […]
Founder Tom Kartsotis created the company to import fashion watches from China to retail in the US. Having founded the brand to import watches, along with his brother, he had soon begun importing leather goods too. The company’s growth was rapid and in quick succession they acquired Zodiac watches, high-end Swiss brand Michele Watch and […]
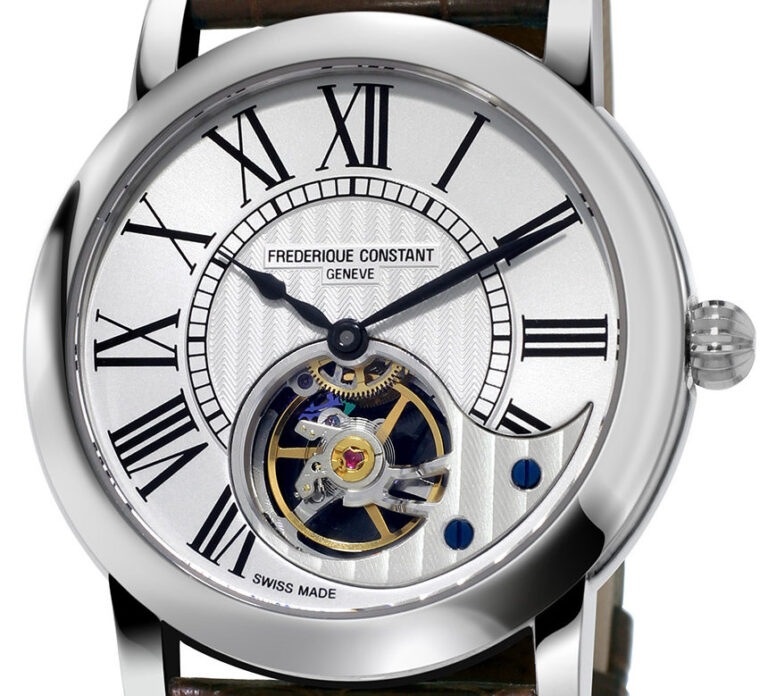
Frederique: Frederique Schreiner 1881-1969 Constant: Constant Stas 1880-1967 The current Managing Director of Frederique Constant S.A., Peter Stas, is a 4th generation descendant of Mr. Constant Stas, who founded his company in 1904, making printed clock dials for the watch industry. Frederique Constant was established in 1988. Aletta Bax and Peter Stas launched their first […]
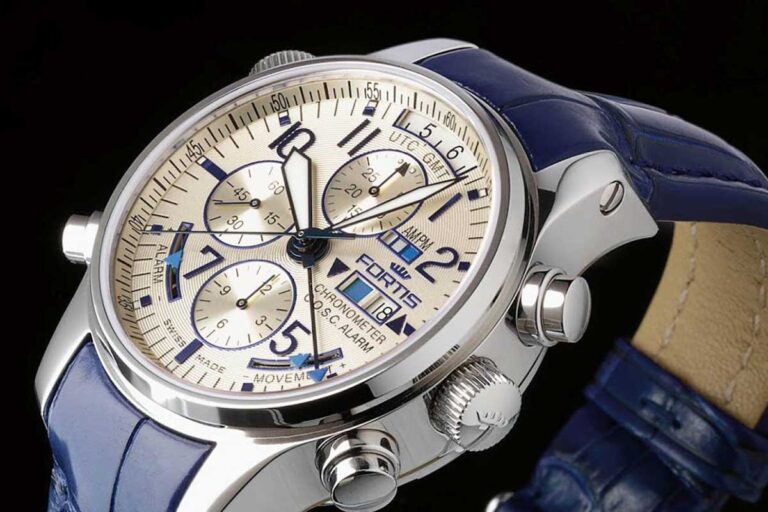
1912 The Swiss village of Grenchen was and still is the residence of FORTIS when the company was founded by Walter Vogt in 1912. Mr. Vogt was a great pacesetter and pioneer: his original beliefs still forms the basis of today’s company’s policy. “..the manufacture of high-quality quality Swiss watches, in innovative designs at inexpensive […]
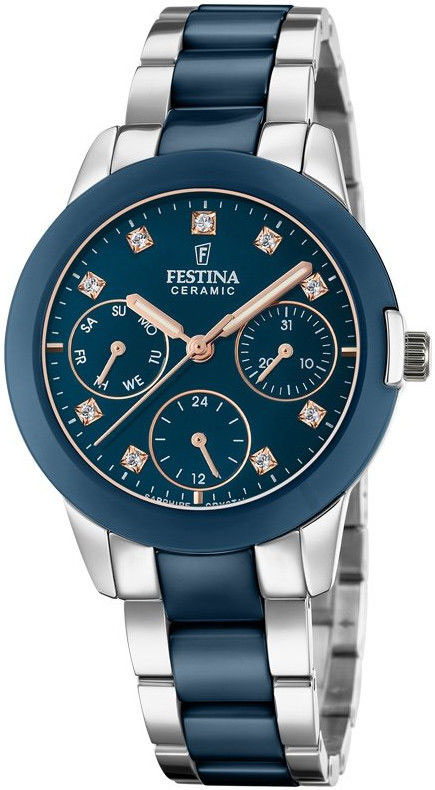
Festina, a Swiss watch manufacturer, was established in the year 1902. It is the certified timekeeper of the Tour de France. Being over 100 years old, it comes among the leading names in Europe and also a a best seller in its home country of Spain. At the moment, the Festina brand carries on its […]
Eterna is a Swiss luxury watch company founded in Grenchen, Canton Solothurn, on 7 November 1856 by Josef Girard and Urs Schild.[1] The company is now owned by Hong Kong-based Citychamp Watch & Jewellery Group Limited, an investment holding company formerly known as China Haidian Holdings- The name Eterna is synonymous with timepieces of the […]
ETA SA Manufacture Horlogère Suisse develops and produces quartz, mechanical and Swatch watch movements. The company’s headquarters are in Grenchen (Solothurn). ETA Manufacture Horlogère Suisse is the motorist of time at the heart of the Swatch Group www.swatchgroup.com Before becoming a single undertaking in 1985, the ETA SA brand consisted of a number of ébauche factories across […]
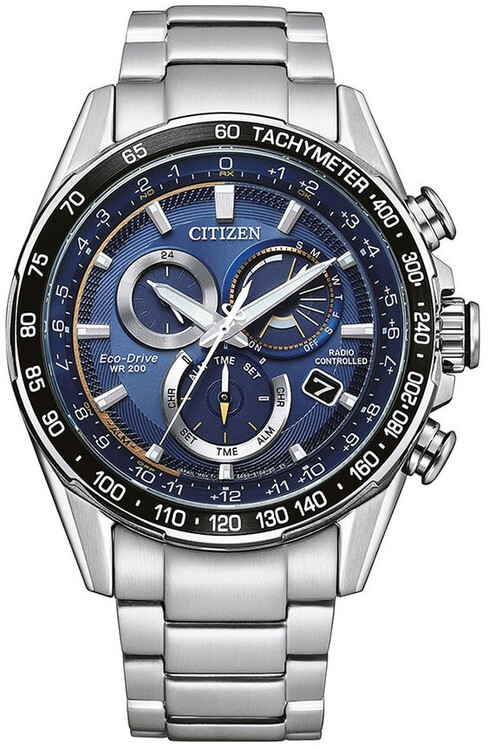
Citizen Watch was originally founded as Shokosha Watch Research Institute in 1918 and is currently known as the manufacturer of CINCOM precision lathe machine tools as well as CITIZEN watches. The trade name originated from a pocket watch CITIZEN sold in 1924. It is one of the world’s largest producers of watches. Today Citizen Watches continues […]
The History of Bovet Watch Founded by Edouard Bovet (1797–1849) who learn the watch making in his early life by his father who was a watchmaker himself. He later in 1814 sent to UK to learn in the school of watch making then to China in 1818 where he made several sale and like the […]
Innocente Binda’s intuition had already alerted him to the potential of a creative approach to publicity, way back in the Thirties. He had several watches with Incaflex movement thrown from the top of the Eiffel Tower, in order to demonstrate the reliability and resistance of the Wyler Vetta products. The movement worked perfectly after being […]
John Arnold is an English watchmakers who born in 1736 and died in 1799. His reputation established as a fine watchmaker when he setup a chronometer factory at Chigwell In 1756 and this give him the credit to bethe first watch maker to design a watch that was both practical and accurate. Here is about […]
The Armani Group is one of the leading fashion and luxury groups in the world today with around 5000 employees and 13 factories. It designs, manufactures, distributes and retails fashion and lifestyle products including apparel, accessories, eyewear, watches, jewelry, home interiors, fragrances and cosmetics under a range of brand names: Giorgio Armani, Armani Collezioni, Mani, […]
Adanac (Canada spilled backward) another one of the military watches which become popular very fast for their simple yet functional design and their sturdy construction. The styling of the watch is very similar, if not identical, to United State Air Force issue Marathon Military Pilot’s Watch. Adanac is (Canada spelled backward) and was produced in the […]
Adidas adidas is a multinational manufacture corporation based at Bavaria Germany. They are famous with their sports product such shoes, clothing and accessories which include the watches. adidas was founded on 18 August 1949 by Adolf Dassler (Adi Dassler) where is adidas get their name from. In 1936 Dassler name become known to the world […]